Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes every time you make a move in your favorite online chess platform? Lichess.org is a popular, free, and open-source chess platform that attracts millions of players worldwide. Its seamless, real-time gameplay experience must be powered by a robust backend infrastructure. In this post, we'll peek behind the curtain and explore the technical processes involved when you play a move.
 Inspecting Network Activity with Chrome DevTools
Inspecting Network Activity with Chrome DevTools
To understand the flow of data when making a move, we'll start by utilizing Chrome DevTools, particularly the Network tab, which allows us to monitor communication between the client (your browser) and the server. For more insights on how to use Chrome DevTools, check out Google's official guide.
 WebSocket Connections
WebSocket Connections
The first notable network activity is a WebSocket connection to a URL similar to: The protocol, wss, indicates an encrypted WebSockets connection using TLS. No surprises here, WebSockets are the obvious choice for real-time browser apps like online chess because they allow for full-duplex communication, enabling instant updates between the client and server without the overhead of repeated HTTP requests.
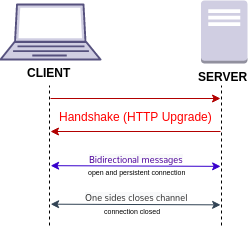
Image: Diagram of WebSocket connection process.
 Local Player's Turn
Local Player's Turn
When we make a move, several packets of data are exchanged. Here's the first packet, sent by us: Clear enough, right? Let's break it down: We then receive the following message: This message from the server acknowledges that it has received our move. Notice that the d field contains the same acknowledgment counter we sent in our move message, in this case, 1. Right after, we receive the following message: This message provides details about the move we just made and the updated game state.
In summary, when a move is made, the client sends a move message, receives an acknowledgment, and then receives a detailed update about the move and the game's new state.
 Opponent's Turn
Opponent's Turn
When the opponent makes a move, we receive a similar packet from the server. One key difference is the dests parameter, which lists all possible moves available from the current position. This parameter is used to highlight the possible moves on the chessboard that we can make after our opponent's move. While these moves could be calculated client-side, providing them server-side ensures consistency - especially for complex or esoteric chess variants - and optimizes performance on clients with limited processing capabilities or energy restrictions.

 Lichess's Architecture
Lichess's Architecture
Lichess's real-time playing system is primarily composed of two main services (both written in Scala):
Architecture Overview
As this implies, lila communicates with lila-ws through Redis, which in turn manages WebSocket connections with clients. If lila is momentarily down, lila-ws can still handle WebSocket connections and maintain real-time communication with clients (perhaps features like chat would still work!). Conversely, if lila-ws is down, the lichess.org website will still be online, but you won't be able to play games. This separation also allows for independent scaling of the two components.

Image: Overview of Lichess's architecture.
Communication using Redis Pub/Sub
The move event is published to a Redis Pub/Sub channel, to which lila is subscribed and processes the move. Redis Pub/Sub offers at-most-once delivery. This means that each message is delivered no more than once to each subscriber, if at all. If a subscriber fails while processing a message, that message is lost and not re-delivered. This has the benefit that once a message is delivered, it can be removed from Redis, reducing memory usage. However, it also means that message loss is possible.
Eventual Data Persistence with MongoDB
While lila primarily stores game states in MongoDB, it optimizes database load by not saving every single move immediately. Instead, it buffers progress by accumulating moves and periodically saving them unless a significant event occurs, such as a game conclusion. This strategy lightens the load on the database while maintaining data integrity.
 Joining a Game In Progress
Joining a Game In Progress
As mentioned earlier, when a player connects, they provide the v parameter, which tells the system the latest version of the game they know about. Since the game state in MongoDB syncs up eventually (and your opponent might move just as you join), a player might initially get a state that's a bit behind the latest action. To handle this, lila-ws uses a trusty java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap: This setup keeps track of all events for any ongoing game and clears them once the game wraps up. It helps players reconnect to an active game by giving them all the events they need from point v onwards, without missing any or doubling up. Understandably, it has to be a concurrency-safe data structure, since multiple threads can be serving multiple players at the same time.

 Wrapping Up
Wrapping Up
We are now ready to sum up the process of making a move in Lichess: The client establishes a WebSocket connection to lila-ws at a URL like wss://socket2.lichess.org/play/.... When a player makes a move, the client sends a move event to lila-ws with details like the move's UCI string and acknowledgment counter. lila-ws responds with an acknowledgment (ack) to confirm that the move has been received. The move event is published to a Redis Pub/Sub channel, to which lila is listening and processes the move. lila receives the move, updates the game state accordingly, and (eventually) stores it in a MongoDB database. An updated game state is then sent back through lila-ws to the client. The client receives the updated game state, reflecting the new move and any changes in the game's status.

Image: Visualization of game state update process.
Remember these 3 key ideas for your startup:
- Utilize WebSockets for Real-Time Communication: For startups developing real-time applications, WebSockets provide a robust solution for seamless, full-duplex communication, ensuring instant updates without the overhead of repeated HTTP requests. Learn more about WebSockets on Mozilla Developer Network.
- Optimize Backend Architecture for Scalability: Lichess's separation of services allows for independent scaling, ensuring that different components can be optimized without affecting the overall system. This approach can be beneficial for startups looking to scale efficiently. For more on scaling architectures, see AWS's guide on scalable web applications.
- Implement Efficient Data Persistence Strategies: By buffering data and saving it periodically, Lichess reduces database load while maintaining data integrity. Startups can adopt similar strategies to optimize performance and resource usage.
For more details, see the original source.






